FXOpen

As a technical indicator, the pivot point is popular amongst traders. It offers valuable insights into price movements and market sentiment. This versatile indicator uses data from the previous period to plot a series of levels that can help traders determine the trend and identify potential support and resistance levels.
Aside from analysing stock chart pivot point levels, traders can employ the same tactics on other financial instruments. For instance, the indicator plays an important role in forex trading.
Regardless of your level of experience, understanding how to calculate and use pivot points in your trading strategy can be a valuable addition to your toolkit. This FXOpen guide aims to impart a comprehensive pivot point definition, explain how to trade them, and detail their potential limitations.
A Deeper Look at Pivot Points
A common question in technical analysis is, “what is a pivot point?” Pivot points trading, or pivot point theory, is a popular technical analysis concept used in a range of financial asset classes, including stocks, currencies, and commodities. The indicator assists traders in gauging overall market trends and predicting possible support/resistance barriers during the current period.
How to Read Pivot Points
The pivot point high low indicator is static. It consists of three levels: pivot point (P), support (S), and resistance (R). If the price is above the pivot point, it will target resistance barriers. Conversely, if it’s below the pivot, it will move to support levels. Thus, support and resistance levels serve as targets and stop-loss zones. They remain constant throughout the period, enabling traders to plan ahead.
In the EURUSD daily chart below, the price is trading below P; therefore, market sentiment is assumed to be bearish. S1 indicates upcoming areas of interest (support). Should a shift above P occur, bullishness arises, and R1 becomes the liquidity draw (resistance).
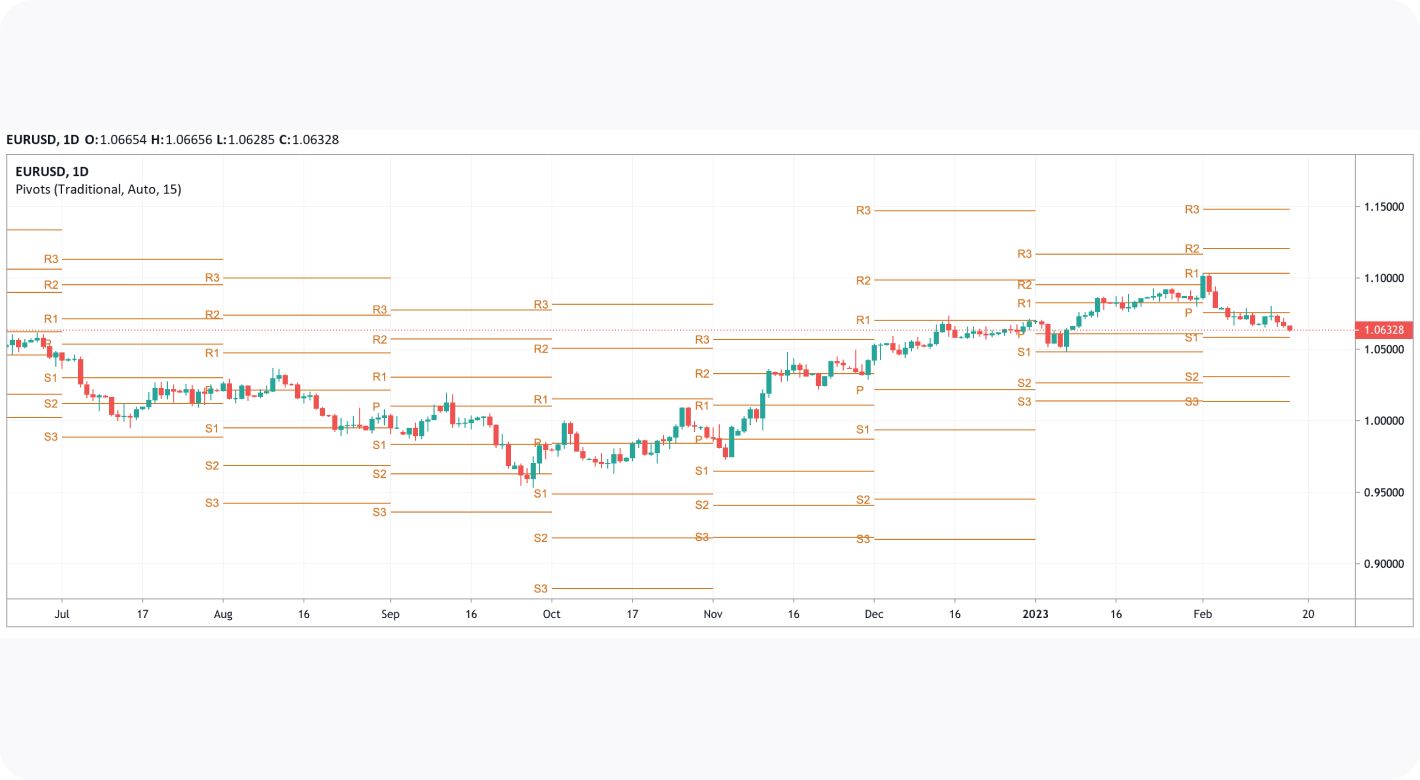
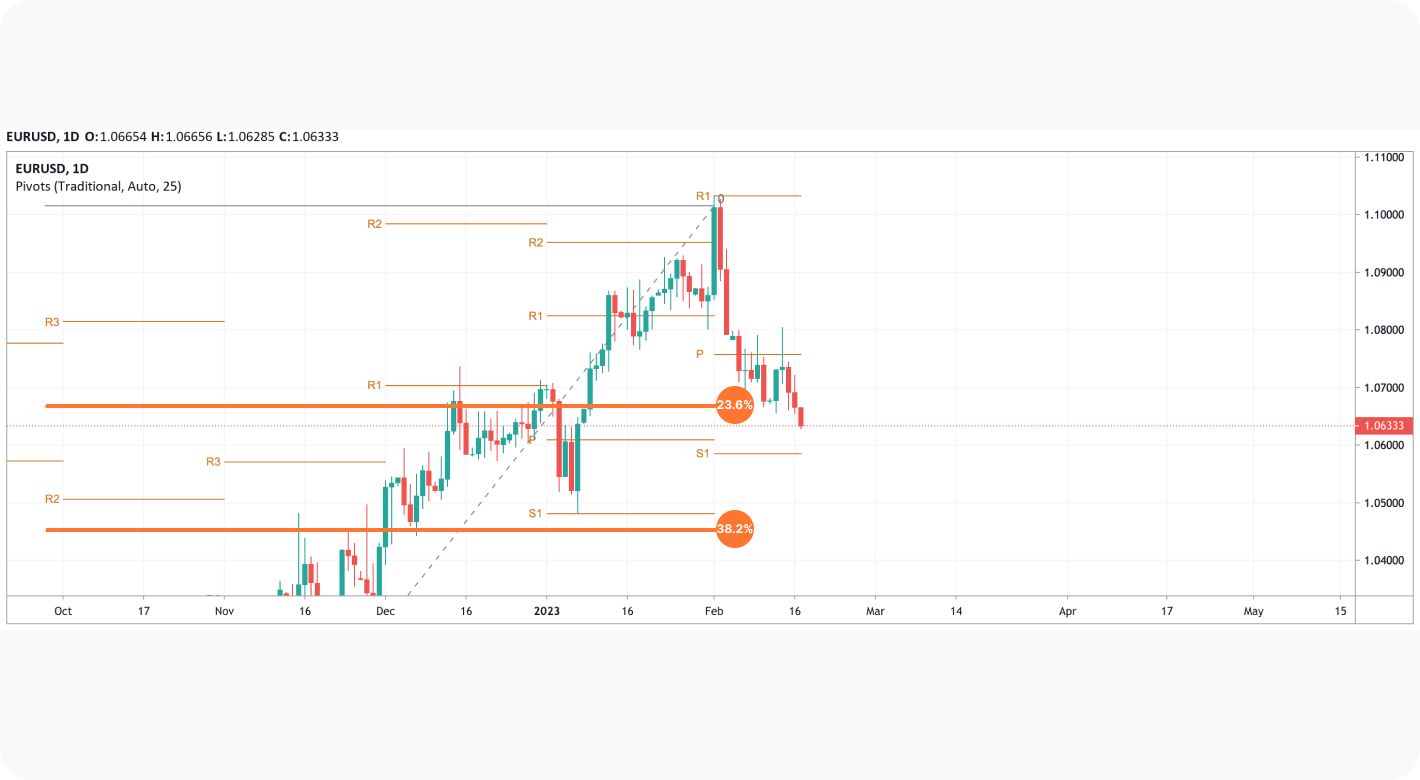
Pivots are widely used with trend indicators such as moving averages and Fibonacci tools. In the chart below, Fibonacci retracements could be used to identify intermediate levels of support and resistance within widely placed pivots.
How to Calculate Pivot Points
There are five key types of pivots. Although they are calculated automatically when implemented on a price chart, it’s worth considering the pivot point calculator formula to understand their differences.
Note the labels for the following formulas:
P = Pivot Point
H = high price
L = low price
C = close price
Traditional Pivot Points
Traders commonly use traditional pivot points in forex or any other market. Traditional pivots identify potential levels of support and resistance by averaging the previous trading period's high, low, and close. Although they are effective, they can produce false signals and lead to incorrect trades in ranging markets and during periods of high volatility.

Woodie’s Pivot Points
Woodie's pivots are similar to standard pivots but include a slight modification to the calculation. In Woodie's method, the close price is assigned more weight.

Camarilla Pivot Points
Camarilla pivots take into account the volatility of the previous trading period to produce pivot levels closer to the current price and thus make them more accurate in short-term trading.

Fibonacci Pivot Points
Fibonacci pivots are based on the Fibonacci sequence, a popular mathematical concept in technical analysis.
They are calculated in the same way as the traditional indicator. However, the levels of support and resistance are determined by adding the Fibonacci sequence with close monitoring of the 38.2% and 61.8% retracement levels as the primary price points.

Trading with the Pivot Points Indicator
There are common rules traders use pivots in trading:
Day trading with pivot points is usually implemented for M30 and shorter intraday timeframes, where pivots are calculated on the previous day's high, low, and close prices. Levels are updated daily, allowing traders to react promptly to market changes and adjust their strategies.
When looking at a long-term analysis, weekly pivots are added to H1, H4, and D1 charts. These are calculated using the previous week's high, low, and close prices, which remain unchanged until the start of the following week.
For further longer-term analysis, traders use monthly pivots on weekly charts. These levels, gathered from the previous month's data, offer a broader picture of market trends and price movements over time.
Also, we can approach trading with the indicator in two common ways – breakout and reversal trading.
The Breakout Trading Strategy
The breakout approach seeks to take advantage of market momentum by entering trades when prices break above or below significant levels of support and resistance.
Bullish Breakout
When levels P and R1 are broken and the price closes above either, it’s more likely a rise will occur.
Bearish Breakout
When levels P and S1 are broken and the price closes below either, it’s more likely the price fall will occur.
Strong momentum and high volume in the market are two critical factors needed for a price rally in both cases.
Trading Conditions
If a breakout is confirmed, traders can enter a trade in the breakout direction (1). A take-profit target is usually placed at the next pivot level (2). A stop-loss level can be placed below the support in a buy trade or above the resistance in a sell trade, or calculated according to a risk/reward ratio. Traders need to continuously monitor their trades and adjust their stop-loss levels to lock in profits as prices move in their favour.
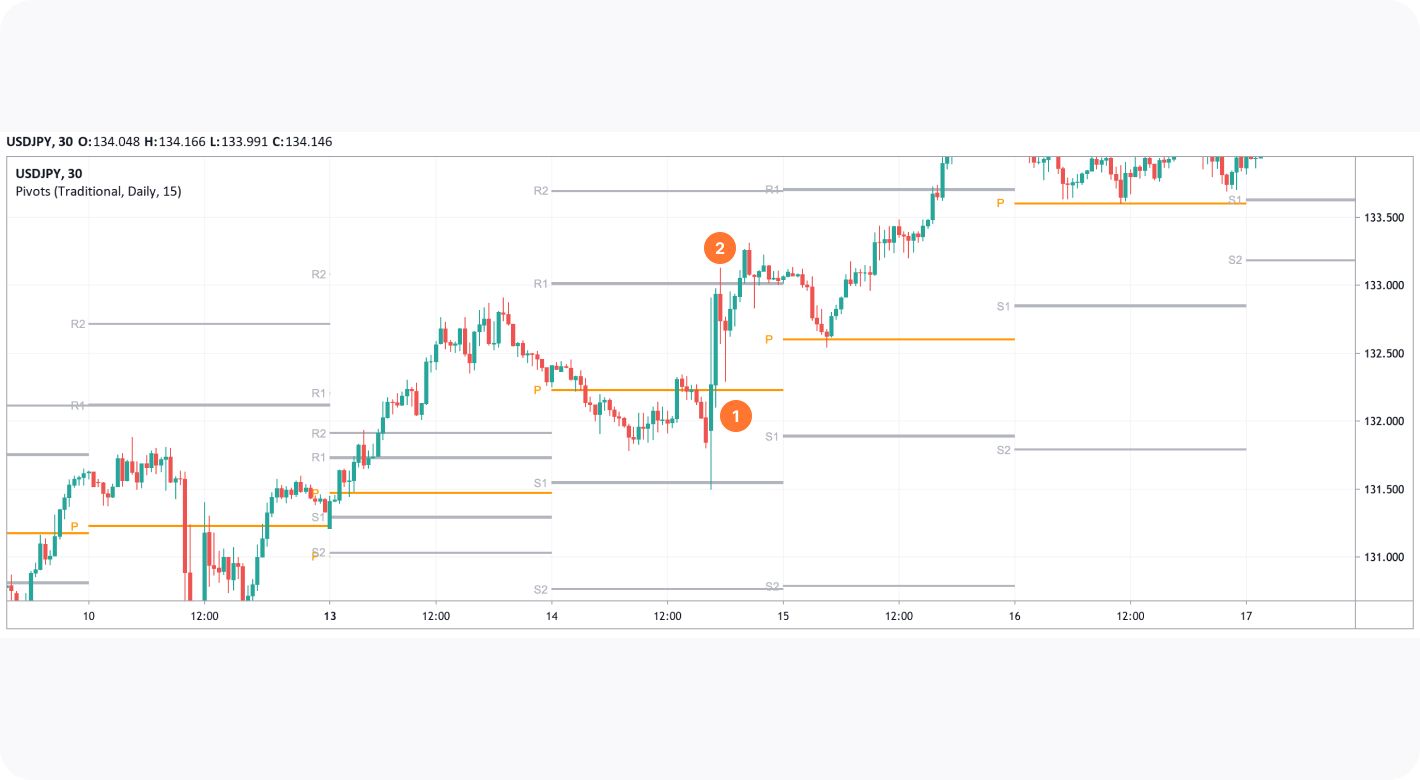
The Reversal Trading Strategy
The reversal strategy seeks to take advantage of a slowdown in market momentum by entering trades when prices stall at significant levels of support or resistance. This signifies a shift in sentiment and willingness for market-makers to drive the price higher.
Bullish Reversal
When levels S1 and S2 are not broken and the price stalls above either, a reversal is more likely to occur.
Bearish Reversal
When levels R1 and R2 are not broken and the price stalls below either, a reversal is expected to happen.
Trading Conditions
If a reversal is confirmed, you can enter a trade in its direction (1). The next level will become a take-profit target (2), which can be trailed to the next level (3) if the market conditions signal a continuation of a price move. A stop-loss level can be placed below a swing low, or above a swing high, depending on the direction of the trade.
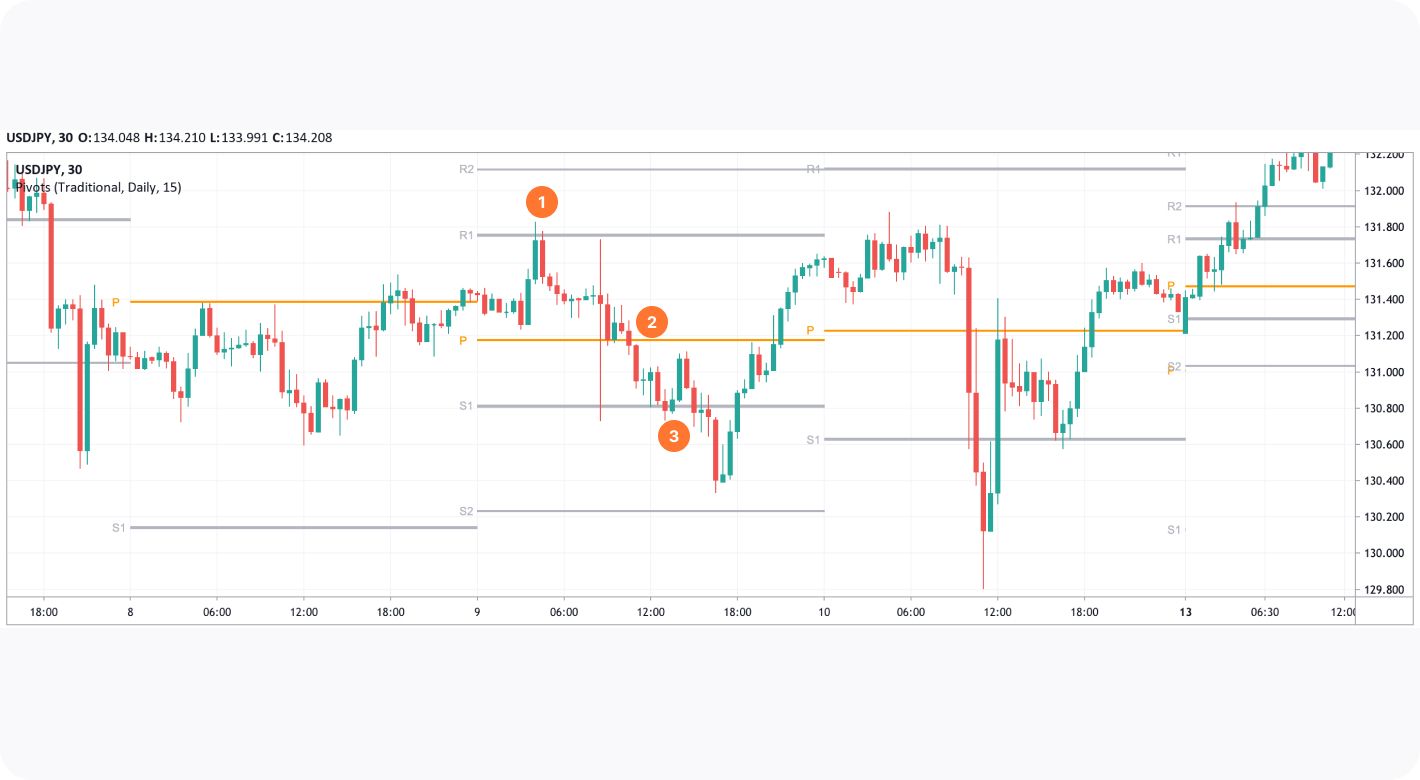
Limitations
Certain limitations exist that we should be mindful of, despite the popularity and usefulness of this indicator.
Firstly, reliance on a single day's data leaves pivots susceptible to one-time events. To circumvent this, traders may use additional technical analysis tools. Moreover, false signals can be delivered in ranging or volatile markets, leading to incorrect signals.
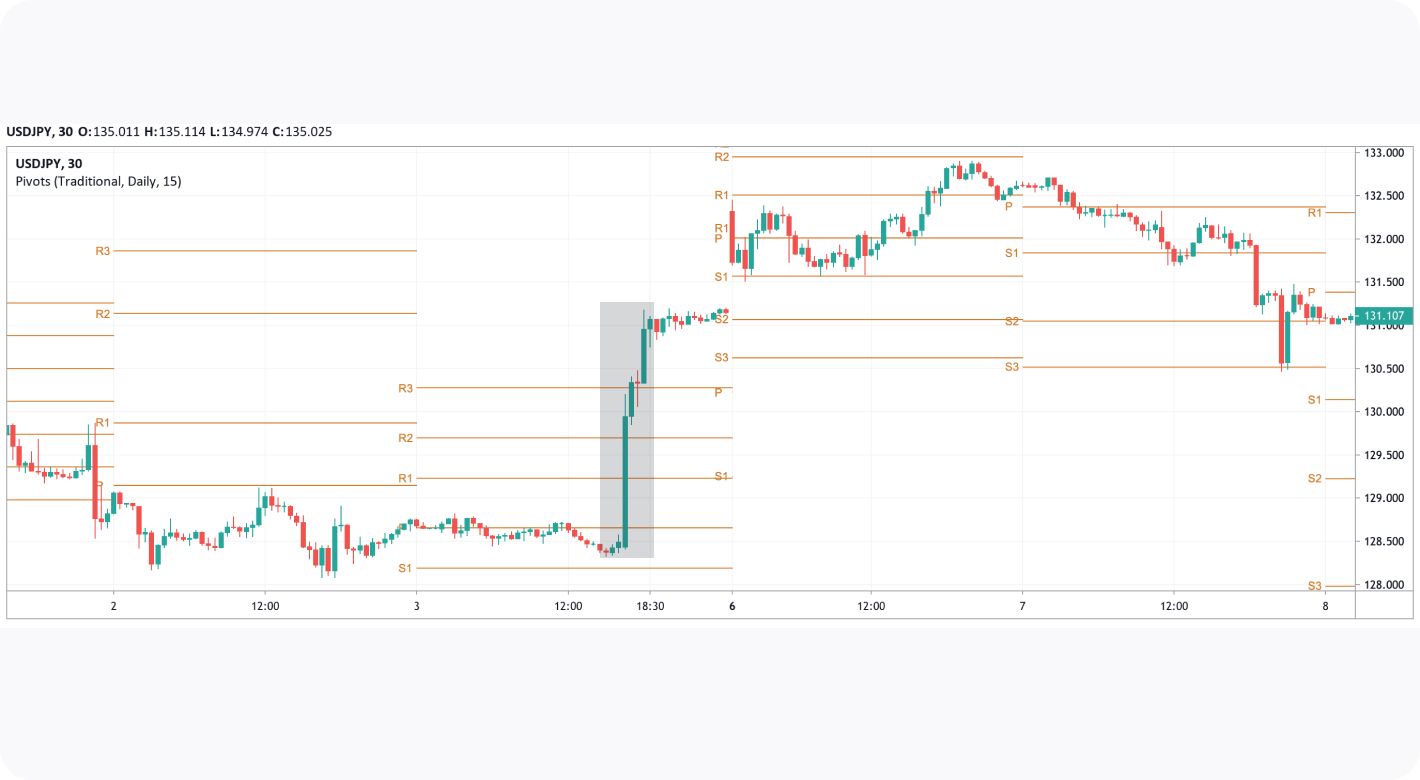
The image below frames a narrative showing how news can result in pivot levels not being respected. The Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP) news event drove USDJPY prices higher without hesitation, completely ignoring R1, where no resistance was exhibited.
Final Thoughts
You can easily implement pivot points in stock trading as well as in commodity, cryptocurrency*, and currency markets. While they can be useful tools, their limitations cannot be overlooked. Gaining a comprehensive understanding of sentiment requires complementary assessment within differentiated timeframes. You can put your newly acquired knowledge to the test by opening an FXOpen account and beginning to test the strategies with pivot points on the TickTrader platform.
*At FXOpen UK and FXOpen AU, Cryptocurrency CFDs are only available for trading by those clients categorised as Professional clients under FCA Rules and Professional clients under ASIC Rules, respectively. They are not available for trading by Retail clients.
This article represents the opinion of the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand only. It is not to be construed as an offer, solicitation, or recommendation with respect to products and services provided by the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand, nor is it to be considered financial advice.
Stay ahead of the market!
Subscribe now to our mailing list and receive the latest market news and insights delivered directly to your inbox.








