FXOpen

The Santa Claus rally is a seasonal phenomenon that refers to the rise in the stock market at the end of each year. While it is a repeated pattern, it has exceptions that are caused by a range of factors.
Why does Christmas push the stock market up? Why are there exceptions? What can happen in the market in 2025? In this article, we try to answer all these questions. Read on to learn more about the Santa Claus stock market rally.
What Is the Santa Claus Rally?
The Santa Claus rally, or simply the Santa rally, refers to a seasonal trend where stock markets often rise during the last five trading days of December and the first two trading days of January. For instance, Santa Claus rally dates for 2025 and 2026 spans from 24 December 2025 to 5 January 2026, covering the final five trading days of 2025 and the first two trading days of 2026, with markets closed on 25 December 2025 and 1 January 2026.
First identified by Yale Hirsch in 1972 in the Stock Trader’s Almanac, this phenomenon has intrigued traders for decades. While not a guaranteed outcome, it has shown a consistent pattern in market data over the years, making it a point of interest for those analysing year-end trends. This trend isn’t limited to the US; global indices often experience similar movements, further highlighting its significance.
In Santa rally history, average returns are modest but noteworthy. Over the past 25 years, a Santa Rally has happened in roughly 70% of years. Since 1969, the S&P 500 has historically gained around 1.3%, according to Stock Trader's Almanac, outperforming most other weeks of the year.
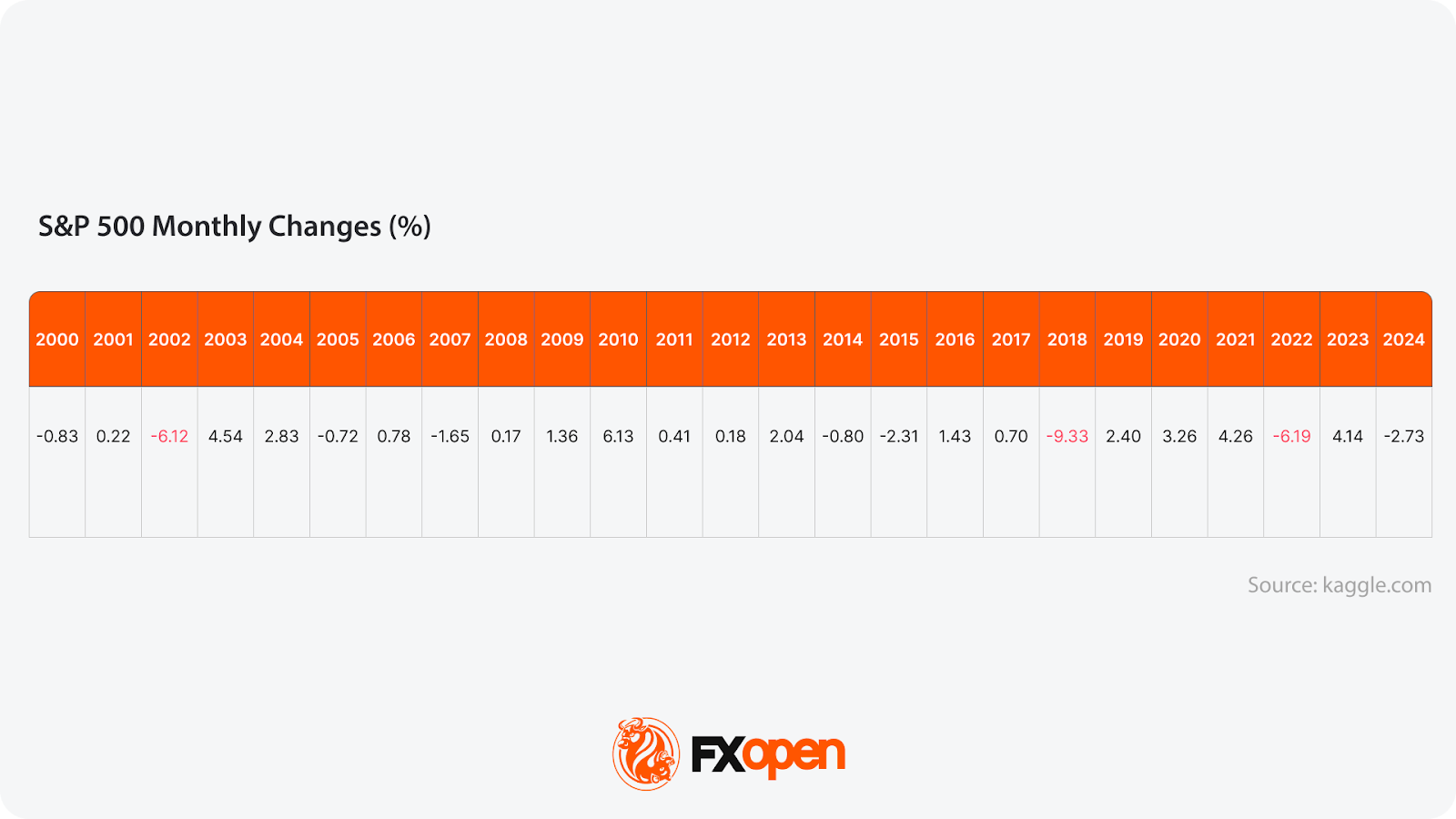
But when you look at the entire month of December, results are mixed. For example, in 2002, the S&P 500 dropped nearly 6%; 2018 was one of the worst Decembers — down about 9%; in 2022, the market fell by over 6% (source: kaggle).
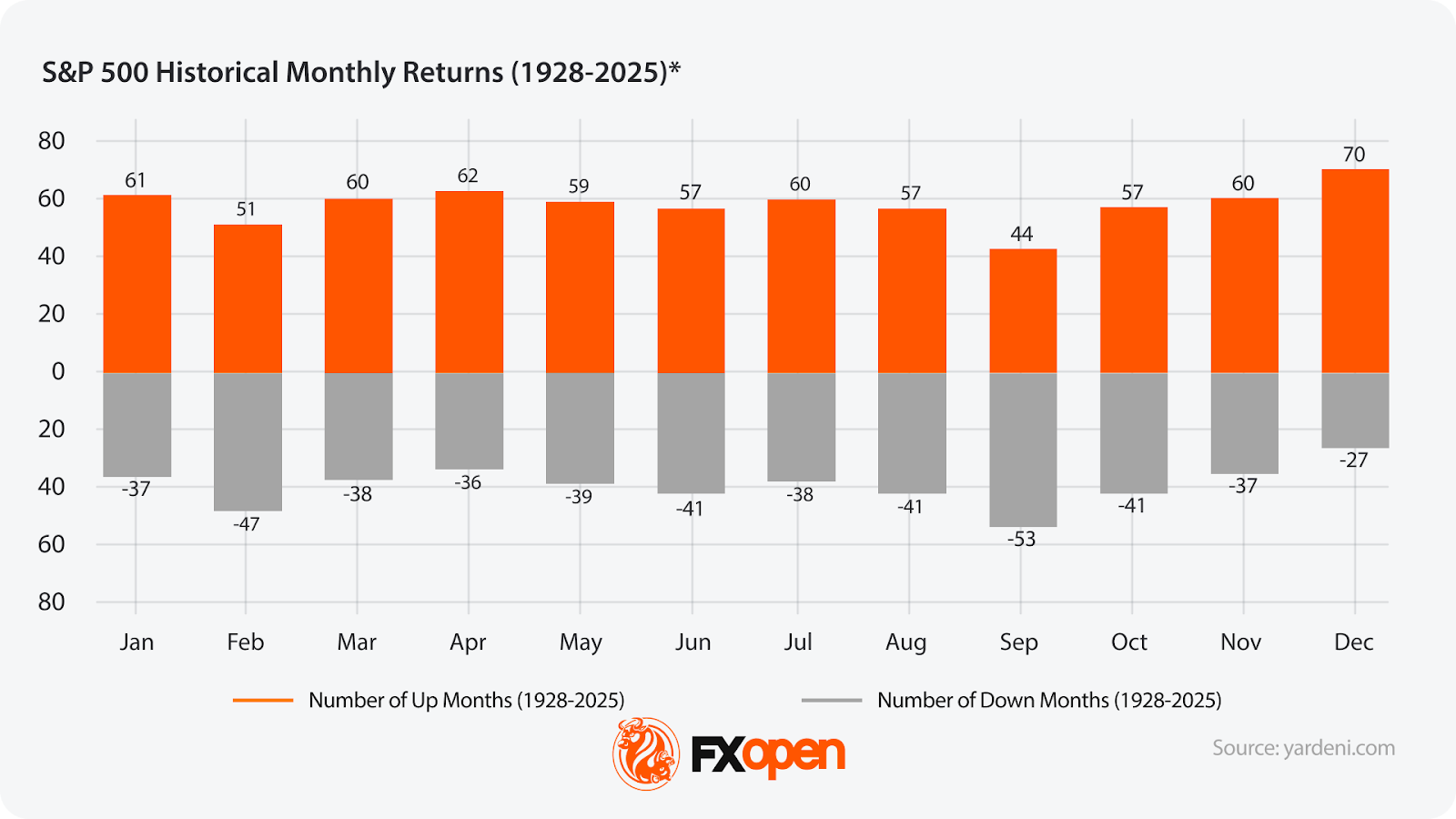
In December stock market history, December shows positive returns in 70 out of the past 97 years, but this still leaves plenty of room for volatility (source: Yardeni Research).
To check market dynamics, you can consider heading over to FXOpen’s TickTrader trading platform.
The Christmas rally in the stock market is believed to stem from several factors. Low trading volumes during the holiday season, as many institutional investors take time off, may reduce resistance to upward price movements. Retail investors, buoyed by end-of-year optimism or holiday bonuses, may drive additional buying. Additionally, some investors reposition portfolios for tax purposes or adjust holdings ahead of the new year, contributing to the upward momentum.
However, this pattern is not immune to disruption. Broader economic events, geopolitical tensions, or bearish sentiment can easily override it. While the Santa Claus rally is a fascinating seasonal trend, traders view it as one piece of the larger market puzzle rather than a reliable signal on its own.
Why Might the Santa Claus Rally Happen?
The Santa Claus rally isn’t a random occurrence. Several factors, both psychological and practical, can drive this year-end market trend. While it doesn’t happen every year, when it does, there are usually clear reasons behind it.
Investor Optimism and Holiday Sentiment
The holiday season often brings a wave of positive sentiment. This optimism can influence traders to take a bullish stance, especially as many are eager to start the new year on a strong note. Retail investors, in particular, may view this period to prepare for potential price fluctuations in January. The festive atmosphere and the prospect of year-end “window dressing”—where fund managers buy well-performing stocks to improve portfolio appearances—can also contribute.
Tax-Driven Portfolio Adjustments
As the year closes, many investors engage in tax-loss harvesting, selling underperforming assets to offset taxable gains. Once these adjustments are complete, reinvestments into higher-performing or promising stocks may push markets higher. This activity can create short-term demand, fuelling upward momentum during the rally period.
Lower Trading Volumes
Institutional investors often step back during the holidays, leaving markets dominated by retail traders and smaller participants. Lower trading volumes can result in less resistance to price movements. With fewer large players balancing the market, price shifts may become more pronounced.
Bonus Reinvestments and End-of-Year Contributions
Many professionals receive year-end bonuses or make final contributions to retirement accounts during this period. Some of this money flows into the markets, adding buying pressure. This effect is particularly noticeable in December, as investors seek to take advantage of market movements before the year wraps up.
How Christmas Impacts Stock Markets
The Christmas period is unique in the trading calendar, shaping market behaviour in ways that stand out from other times of the year. While some effects align with holiday-driven sentiment, others reflect broader seasonal trends.
Sector-Specific Strength
The most popular Christmas stocks tend to be those in the consumer discretionary and retail sectors (though this isn’t guaranteed). The holiday shopping boom tends to drive significant revenues for companies in these sectors, often lifting their stock prices. Many consider companies like Amazon and brick-and-mortar retailers to be among the most popular stocks to buy before Christmas, given they often see increased trading interest around the holidays and a potential Christmas rally.
A strong showing in retail sales, especially in countries like the US, can bolster market indices tied to consumer spending.
Economic Data Releases
The Christmas season still sees the publication of economic indicators. While there are no specific year-end releases from government statistical bodies, some 3rd-party reports may have an impact. Likewise, scheduled publications, such as durable goods orders or FOMC meeting minutes, can affect sentiment. Positive data can provide an additional boost to stock markets in December. However, weaker-than-expected results can dampen enthusiasm, counteracting any seasonal cheer.
International Variations
While Western markets slow down for Christmas, other global markets may not follow the same pattern. For instance, Asian markets, where Christmas is less of a holiday, may see regular or even increased activity. This discrepancy can create interesting dynamics for traders who keep an eye on global portfolios.
The "Post-Holiday Rebound"
As Christmas wraps up, markets often experience a slight rebound leading into the New Year, driven by renewed investor activity. This period, while brief, is closely watched as it can set the tone for the opening days of January trading.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While the Santa Claus rally and year-end trends can be intriguing, they are far from guaranteed. Relying solely on these patterns without deeper analysis can lead to overlooked risks.
Uncertain Market Conditions
Macro factors, like interest rate changes, geopolitical tensions, or unexpected economic data, can disrupt seasonal trends. For instance, during times of economic uncertainty, the optimism often associated with the holidays might not translate to market gains. Traders must account for these broader dynamics rather than assuming the rally will occur.
Overemphasis on Historical Patterns
Historical data can provide valuable insights, but markets evolve. A pattern that held up in past decades may not carry the same weight today due to shifts in investor behaviour, technological advancements, and globalisation. Traders focusing too heavily on past trends may miss the impact of more relevant, current developments.
Low Liquidity Risks
The reduced trading volumes typical of the holiday season can work both ways. While thin markets may allow for upward price movements, they can also lead to heightened volatility. A single large trade or unexpected event can swing prices sharply, posing challenges for those navigating the market during this time.
Sector-Specific Sensitivity
Sectors like retail and consumer discretionary often draw attention during December due to strong sales data. However, poor performance or weak holiday shopping figures can cause a ripple effect, dragging down not only individual stocks but broader indices tied to these sectors.
FOMO and Overtrading
The hype surrounding the Santa Claus rally can lead to overtrading or ill-timed decisions, particularly for less experienced traders. Maintaining a disciplined approach, combined with clear risk management strategies, may help mitigate this issue.
The Bottom Line
The Santa Claus rally is a fascinating seasonal trend, offering insights into how market sentiment and activity shift during the holidays. While not guaranteed, understanding these patterns may help traders develop their strategies.
If you’re exploring seasonal trends in stock CFDs or trade forex and commodity CFDs, you can consider opening an FXOpen account today to access more than 700 markets, over 1,200 trading tools, tight spreads, and low commissions from $1.50.
FAQ
What Is the Santa Claus Rally?
The Santa Claus rally refers to a seasonal trend where stock markets often rise during the final week of December and the first two trading days of January. It’s a well-documented phenomenon, first identified by Yale Hirsch in the Stock Trader’s Almanac. While it doesn’t occur every year, Santa Claus rally history demonstrates consistent patterns, with the S&P 500 averaging a 1.3% gain during this period.
What Are the Dates for the Santa Claus Rally?
The Santa Claus rally typically covers the final five trading days of December and the first two trading days of January. The Santa Claus rally in 2025 runs from 24 December through 5 January 2026, encompassing the last five trading days of 2025 and the first two trading sessions of 2026, with market holidays on 25 December and 1 January.
How Many Days Does the Santa Claus Stock Rally Take?
The rally spans seven trading days: the last five of December and the first two of January. While its duration is fixed, the intensity and consistency of the trend vary from year to year.
Is December Good for Stocks?
Historically, December has been one of the strongest months for stock markets. Positive sentiment, strong retail performance, and tax-related portfolio adjustments often contribute to this trend. According to Yardeni Research, December shows positive returns in 70 out of the past 97 years, but this still leaves plenty of room for volatility.
Is the Stock Market Open on Christmas?
No, US and UK stock markets are closed on Christmas Day, with reduced hours on Christmas Eve.
Watch our video: “Santa Rally or Santa Crash? What History Says About December Volatility”
This article represents the opinion of the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand only. It is not to be construed as an offer, solicitation, or recommendation with respect to products and services provided by the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand, nor is it to be considered financial advice.
Stay ahead of the market!
Subscribe now to our mailing list and receive the latest market news and insights delivered directly to your inbox.








