FXOpen

Momentum indicators are important tools for traders seeking to evaluate the strength and speed of price movements. These technical analysis instruments are used by traders to identify potential entry and exit points, confirm market signals, and filter market noise. In this article, we review five momentum indicators that remain widely used by traders to support them in their decision-making in volatile markets.
What Is a Momentum Indicator?
Momentum in technical analysis refers to the rate at which an asset's price accelerates or decelerates. Understanding momentum may assist traders in identifying potential trend continuations or reversals.
A momentum indicator is a technical analysis tool that measures how quickly and strongly an asset’s price is moving. Instead of showing the direction of the trend, it highlights the strength behind price movements. By comparing price changes over a set period, momentum indicators can help traders see if a market is gaining or losing strength. This information is often used to spot potential overbought or oversold conditions and to identify possible entry or exit points.
A stock momentum indicator like the Relative Strength Index (RSI), for instance, may indicate that stocks are currently bought or sold too heavily and their price is due for a reversal.
The Significance of Momentum Technical Indicators
Momentum indicators do not focus on the direction of the price movement, but rather on the strength behind it. They’re able to quantify and represent hidden clues about the future market direction. By learning to read momentum indicators, traders can develop trading strategies and identify conditions for new trades.
Momentum tools produce a range of signals that offer traders an edge over the markets. Let’s take a look at some of the most common momentum signals, including overbought/oversold conditions, divergences, and crossovers.
Overbought and Oversold Conditions
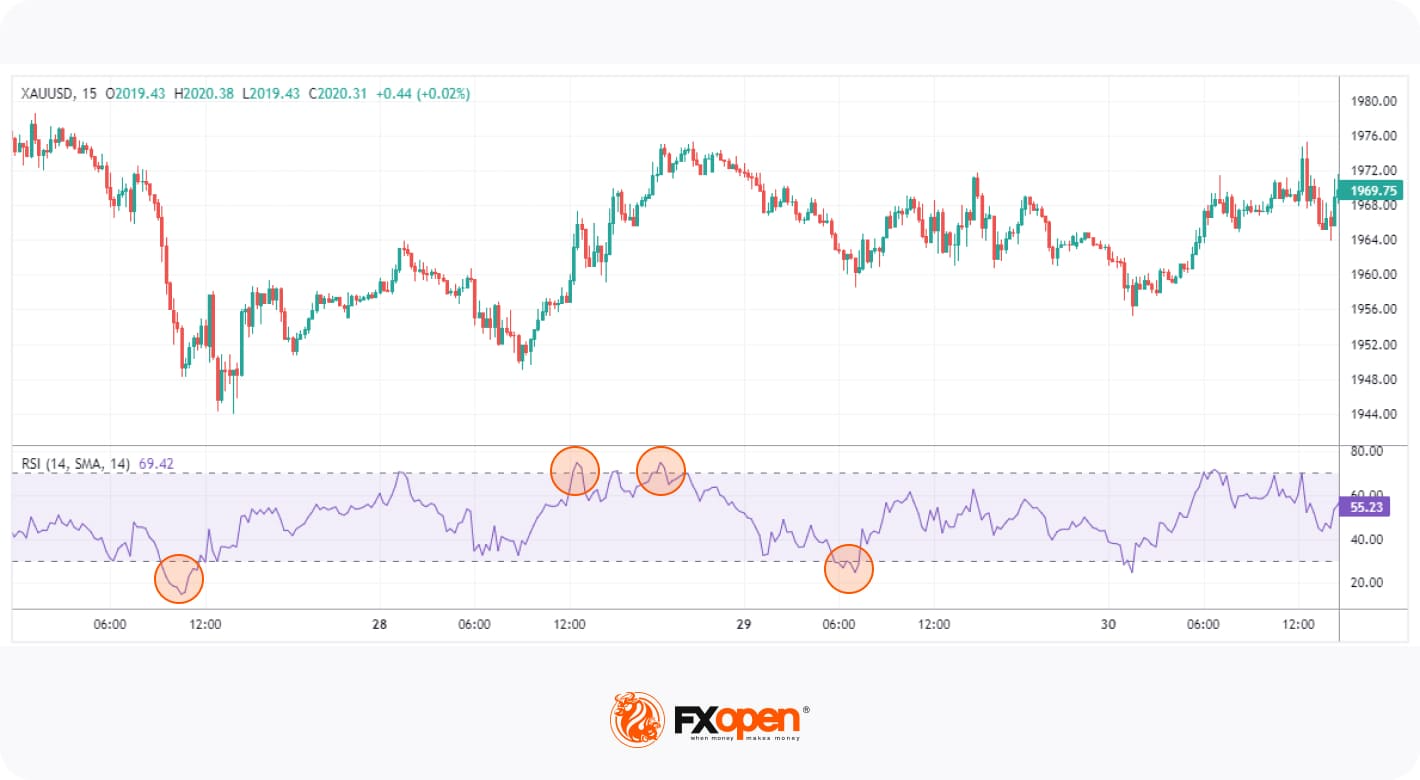
These signals indicate when an asset's price has moved too far in one direction without sufficient support from fundamental or technical factors and is likely to reverse. For example, RSI generates overbought signals when the reading rises above 70 and signals oversold conditions when the reading falls below 30.
Divergence
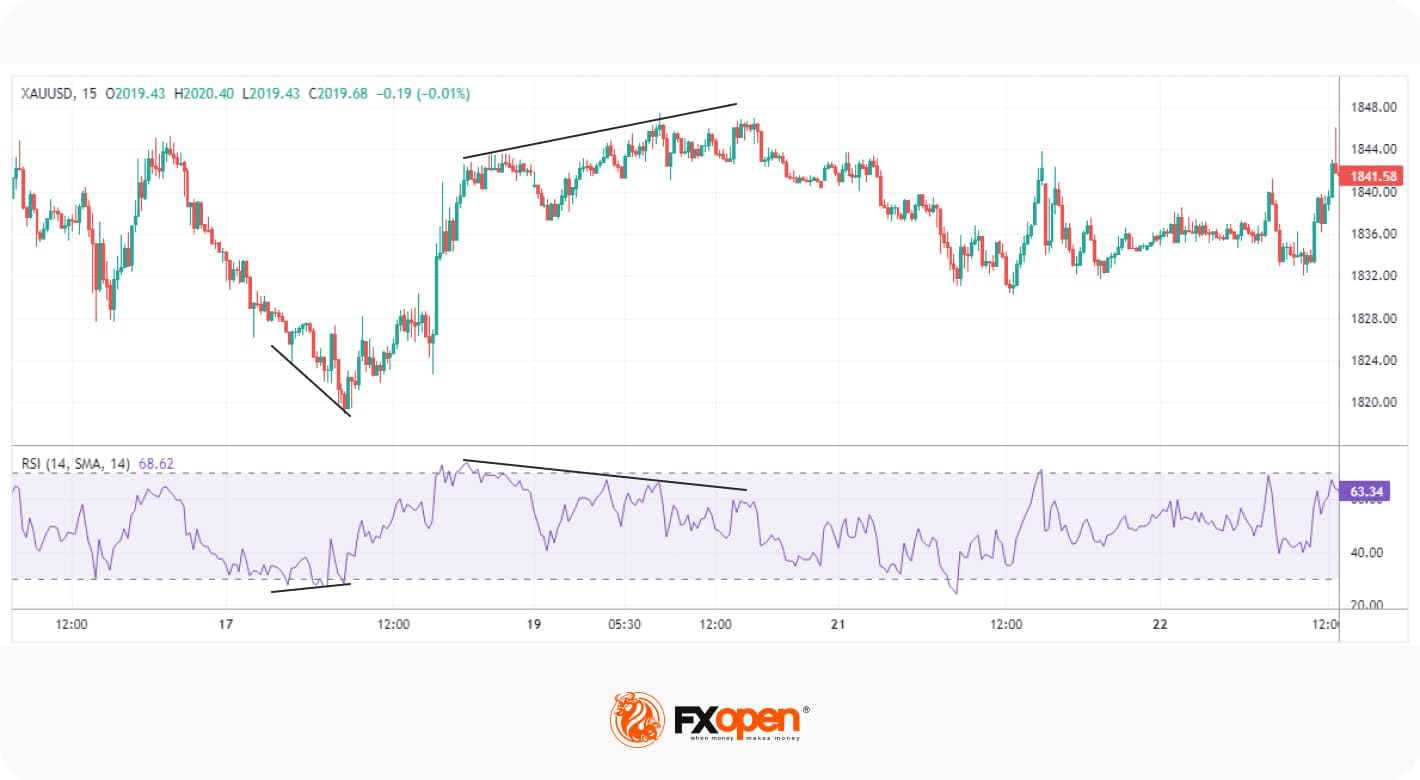
Divergence occurs when the price of an asset moves in the opposite direction of the indicator, suggesting an upcoming reversal. For instance, when the price is making higher highs, but RSI is making lower highs, this indicates a bearish divergence that increases the likelihood of a downward move.
Crossover

These signals are generated when the indicator's lines cross each other or a certain threshold. A common example is the MACD, where traders look for crossovers between the fast MACD line and the slower signal line to spot potential entry and exit points.
List of Five Momentum Indicators for Technical Analysis
Now that we understand the types of signals that momentum tools produce, let’s break down five of the most popular with a momentum indicators list. If you’d like to experiment with them yourself, you’ll find each tool in the TickTrader trading platform.
1. Relative Strength Index (RSI)
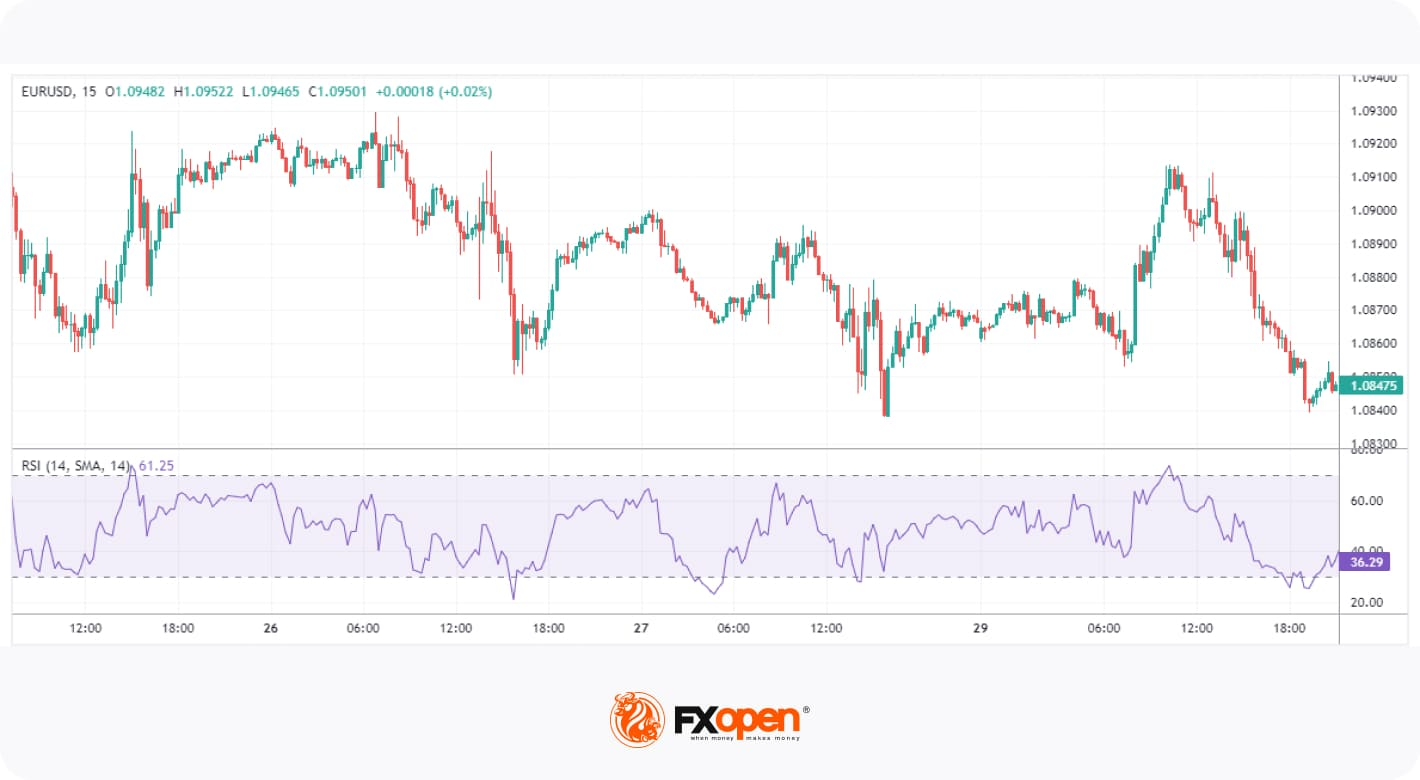
The RSI is one of the most popular and well-documented momentum indicators. It measures the speed and change of price movements by comparing the average gain to the average loss over a specified period, usually 14.
RSI is an oscillator, moving between 0 and 100. Values above 70 reflect overbought conditions, while values below 30 indicate oversold conditions. When the RSI moves out of overbought or oversold territory, many traders interpret this as a reversal confirmation. Sustained movements above or below the midpoint (50) can also be used to confirm a bullish or bearish trend, respectively. Moreover, traders look for divergence between the RSI and price to identify weakening trends and possible reversals.
2. Average Directional Index (ADX)
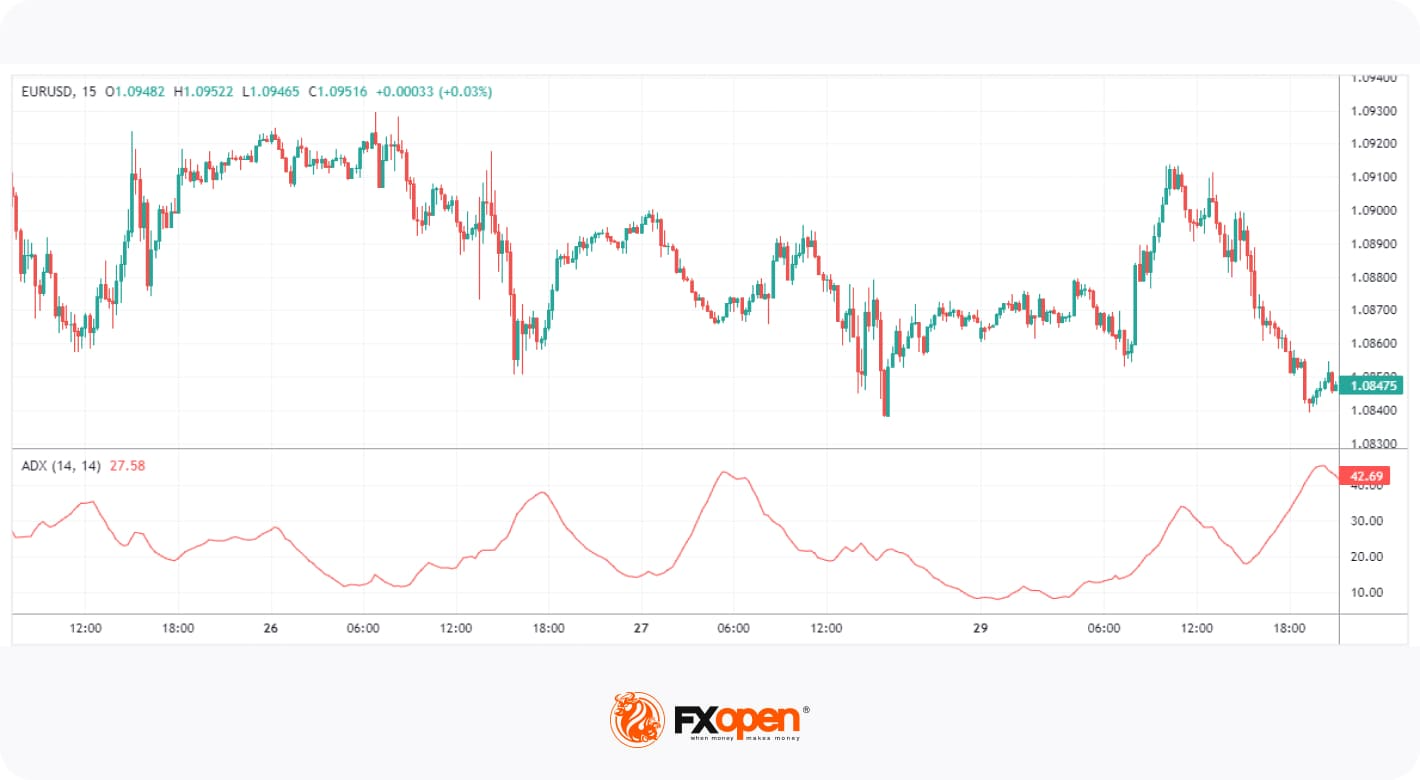
The ADX is a momentum indicator used to determine a trend’s strength. Unlike most other tools, its reading doesn’t move according to the direction of price action, i.e. it doesn’t move up if bullish or down when bearish. Instead, it ranges from 0 to 100, with values above 25 indicating a strong trend and below 25 suggesting a weak or non-trending market.
ADX is commonly used in combination with other tools, as it simply confirms the trendiness of a market. For example, traders might use a leading indicator like RSI to anticipate bullishness and confirm the trend when ADX crosses over 25.
3. Commodity Channel Index (CCI)
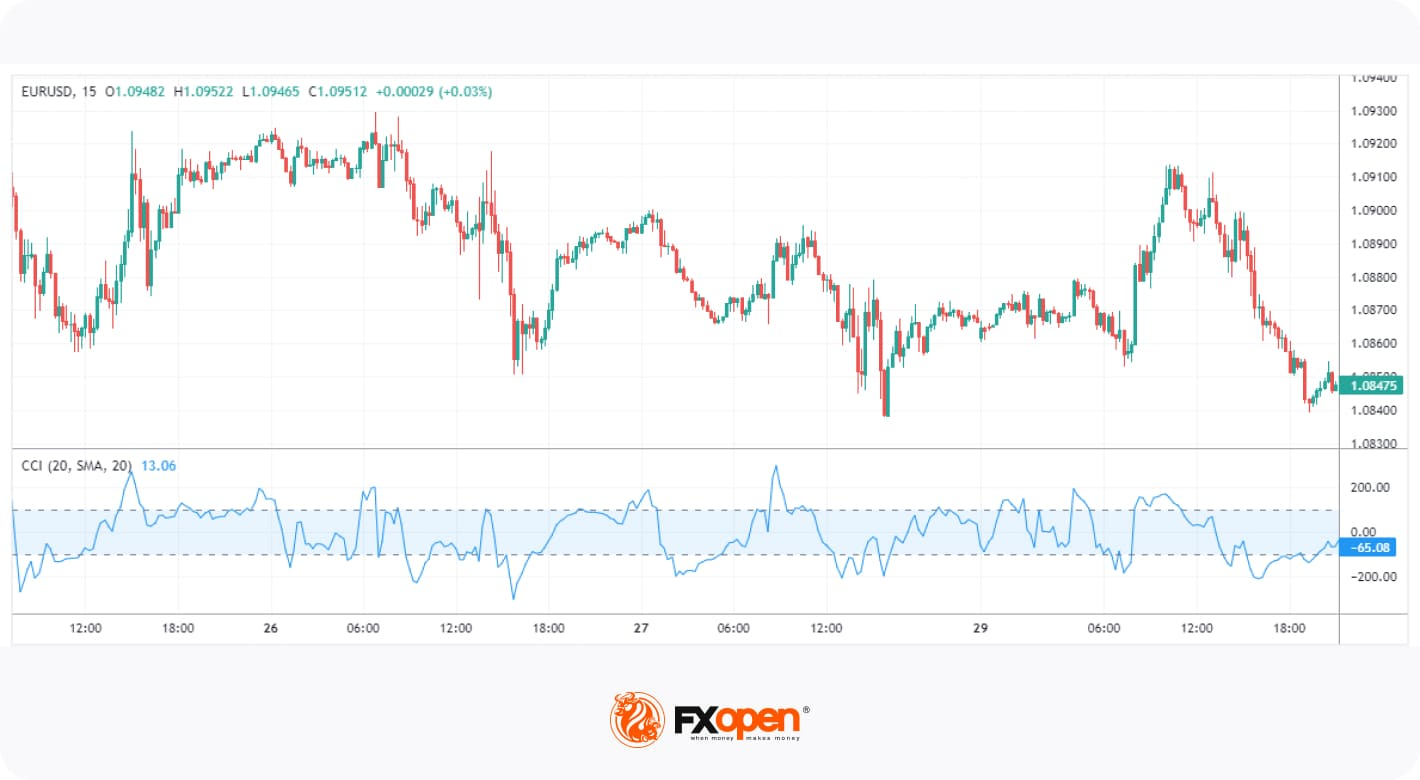
The CCI is a versatile momentum indicator. It uses a constant in its calculation to ensure that 75% of values fall between +/- 100, with moves outside of the range generally indicating a trend breakout or continuation. It can also show extreme overbought or oversold conditions when its value exceeds +/- 200.
The CCI requires a more nuanced approach than other tools and is typically used to confirm a trader’s directional bias. For instance, a visually identifiable bullish trend can be confirmed by looking at the CCI. If its value is skewed toward 100+, traders can be confident in their observation. When the market cools off, CCI will fall below 100. Traders can then confirm a pullback entry with a move back into the +/- 100 range.
4. Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
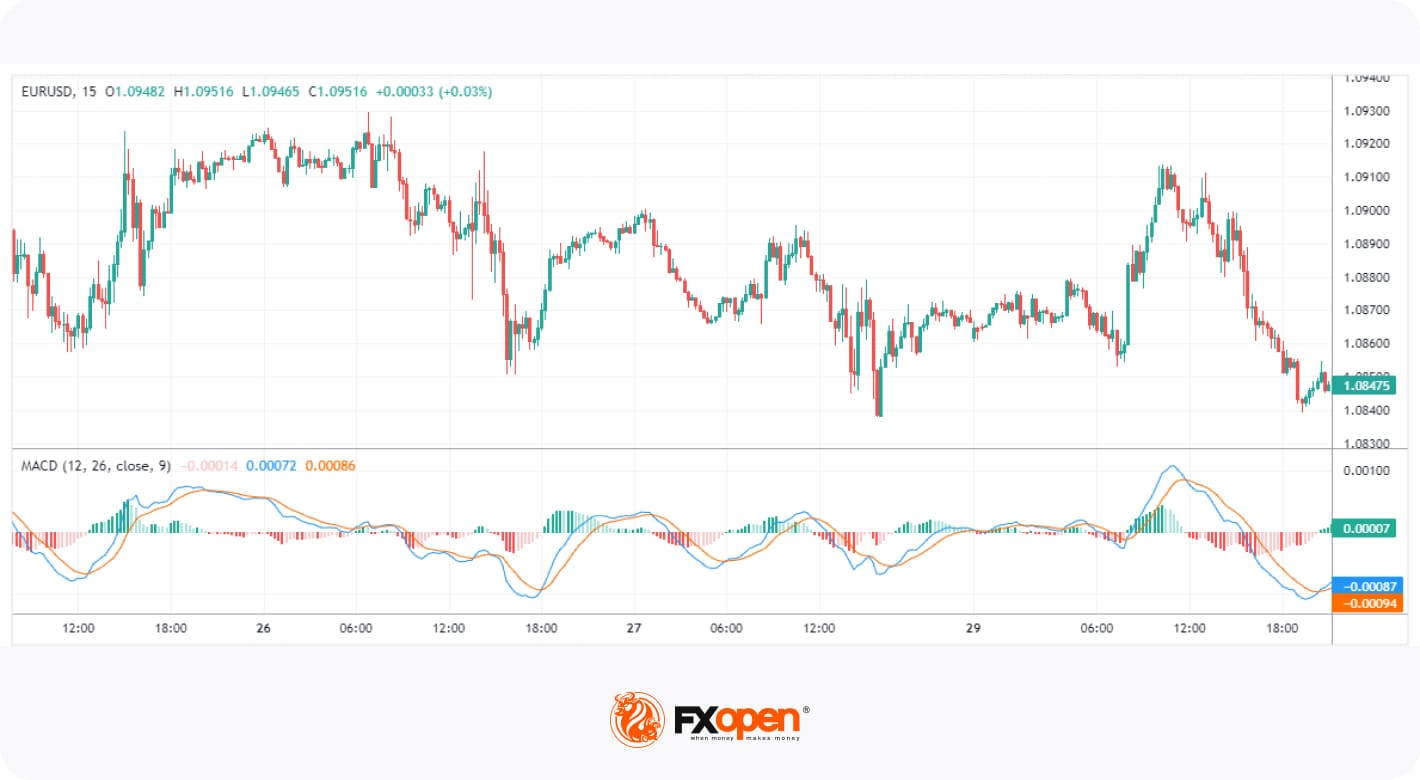
The MACD is a highly regarded trend-following momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages of an asset's price. It’s used in technical analysis to identify the relationship between two moving averages of a security’s price. The MACD reflects the trend’s strength, direction, and duration, as well as possible reversal points.
Traders use crossovers between the MACD and signal lines as potential entry and exit signals. Additionally, when the MACD histogram crosses above or below the zero line, it can indicate bullish or bearish momentum in the market. Lastly, it’s also possible to spot divergences between price and the indicator’s peaks and troughs, similar to how divergences are identified with RSI.
5. Momentum (Mom)
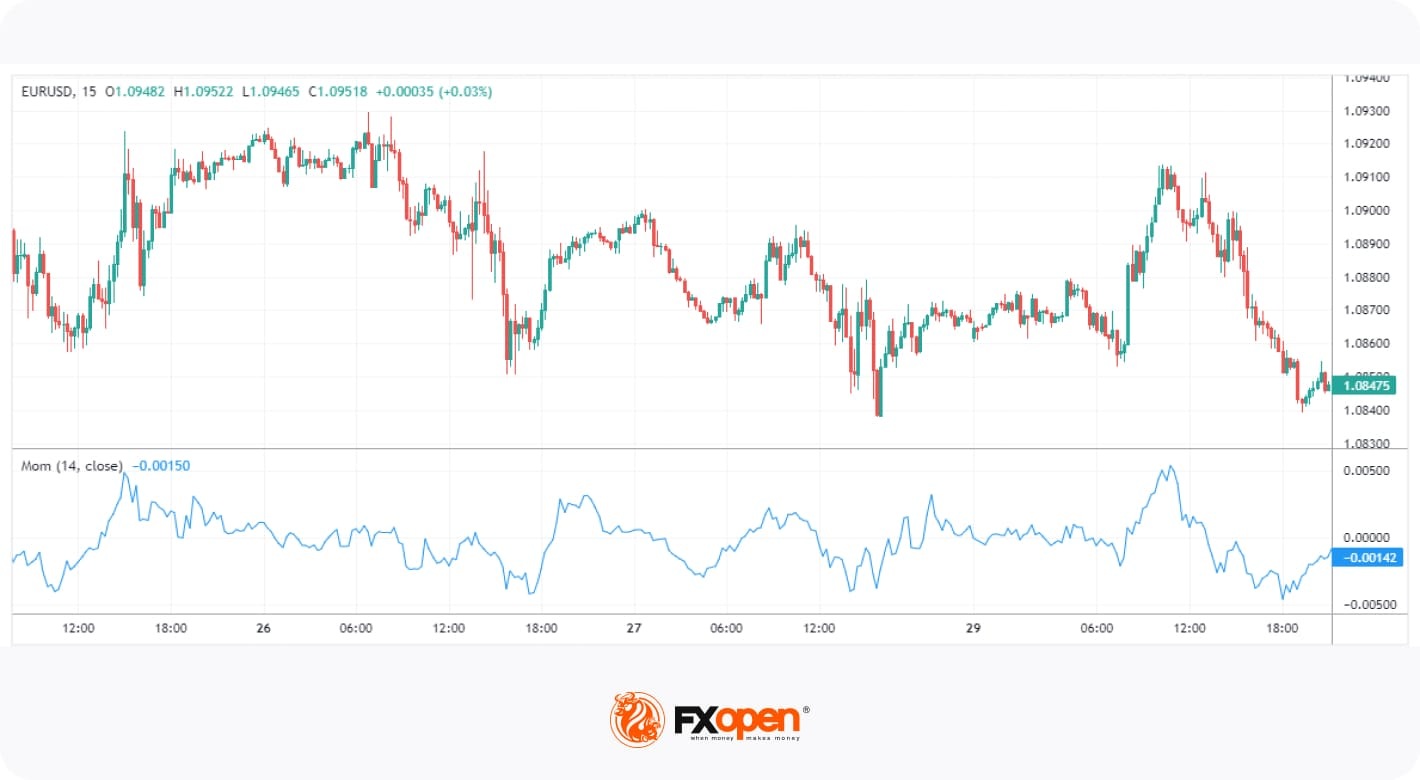
The Momentum indicator is considered a simple tool that measures the rate of change in an asset's price over a specific period. The value of the Momentum depends on the market it’s applied to. For example, using the Momentum indicator in stocks will result in a fluctuating value typically between +/- 20, depending on the stock’s price. For forex pairs, its range may look more like +/- 0.02.
The common feature across all markets, however, is the zero line. Generally speaking, positive Momentum values indicate upward price movement, while negative values suggest downward movement. It can also show overbought and oversold conditions, but its lack of defined boundaries means this can be tricky. However, Momentum is especially useful for identifying divergences.
Advantages of Momentum Indicators
Momentum indicators are valuable tools in technical analysis, reflecting the strength and speed of price movements. They offer several advantages that may improve trading strategies:
- Identify Trends Early: Market momentum indicators can reveal potential shifts in trend direction, providing traders with additional context for evaluating entry and exit points.
- Objective Analysis: They provide quantifiable data, reducing reliance on subjective analysis and emotional decision-making.
- Spot Overbought and Oversold Conditions: Momentum tools show when an asset is overbought or oversold, signalling potential reversals and exit points.
- Confirm Trade Signals: Combining momentum indicators with other technical tools may improve trade signals, providing stronger confirmation for trading decisions.
- Adaptable Across Markets: They can be applied to various assets, including stocks, forex, and commodities, making them versatile tools for traders.
Things to Consider When Trading Momentum Indicators
While momentum indicators may be a helpful addition to any trader’s arsenal, there are a few things to be aware of:
- Trade with the Trend: Trends often last longer than you may think, and constantly looking for trend reversals will only end in frustration. Look for bullish signals during an uptrend and bearish signals in a downtrend.
- Use Multiple Indicators: Relying on a single tool can lead to false signals. Many traders combine a lagging indicator, like MACD, with a leading indicator, like RSI. Combining two or three tools may help confirm signals and improve trade accuracy.
- Beware of False Signals: Momentum indicators can sometimes generate false signals, especially in sideways or choppy markets. Being patient and waiting for confirmation before entering a trade is vital.
- Don’t Rely Too Heavily on Indicators: While momentum indicators may be helpful, relying solely on them without considering price action, market structure, or fundamental aspects can lead to poor trading decisions. Use these indicators alongside other tools for a momentum indicator strategy.
Final Thoughts
Momentum indicators play a critical role in technical analysis, offering traders valuable insights into the strength and direction of market movements. Tools such as RSI, MACD, CCI, ADX, and the Momentum Indicator are widely used to confirm trends, highlight overbought or oversold conditions, and improve entry and exit timing. While no single indicator should be used in isolation, combining these tools with solid risk management and broader market analysis can support traders in their trading decision-making.
If you want to test your strategy with the above-mentioned indicators, you may consider opening an FXOpen account, where you can trade over 700 markets with low costs. Good luck!
FAQ
How May Momentum Indicators Be Used?
Momentum indicators may be used to assess the speed and strength of price movements in a financial market. They can help traders identify potential overbought or oversold conditions, confirm trends, or signal possible reversals. By comparing the current price to previous price levels, momentum indicators provide insights into whether a market move is gaining or losing strength.
What Period is Set for a Momentum Indicator?
If we are talking about the Momentum indicator, the period depends on your trading style. For short-term traders, 7 and 10 periods are common, while long-term traders may prefer 14 and 21 periods. Testing various periods based on asset volatility can improve results.
What Is the Most Popular Momentum Indicator for Scalping?
There is no single most popular momentum indicator for scalping but the Relative Strength Index (RSI) is often favoured by scalpers due to its ability to quickly identify overbought or oversold conditions. Its responsiveness is used by scalpers to make rapid decisions in fast-moving markets.
What Is the Difference Between Momentum and Trend Indicators?
Momentum trading indicators measure the speed of price changes, while trend indicators assess the direction and persistence of price movements. To put it simply, momentum focuses on strength, while trend indicators focus on the overall direction.
Is MACD a Momentum Indicator?
Yes, the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) is one of the most popular momentum indicators, especially in forex and stock trading. It may reveal changes in momentum and help identify potential trend reversals.
This article represents the opinion of the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand only. It is not to be construed as an offer, solicitation, or recommendation with respect to products and services provided by the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand, nor is it to be considered financial advice.
Stay ahead of the market!
Subscribe now to our mailing list and receive the latest market news and insights delivered directly to your inbox.








